How To Check If MySQL Is Installed On Linux (Command line)
When you log in to a Linux server, it’s not obvious which applications are installed. Especially if you are on a server with only a terminal to control it. In this tutorial, I talk specifically about MySQL and tell you how you can quickly check whether the service is already installed or not (and the client too!).
On Linux, the command line “mysqld –version” will return the MySQL server version only if it’s installed on the computer. For the client, the command “mysql –version” can be used to check if the MySQL client is installed. If there is an error (“command not found”), MySQL is not installed.
In this tutorial, I will give you more detail about these commands and answer other important questions, like checking if MySQL is started, and which version or port it’s using on the Linux server.
How to check if MySQL is installed on Linux?
When MySQL client is installed, the “mysql” command is added. The same thing goes for the server installation, with the “mysqld” command. Testing these commands can tell if MySQL is installed on the Linux server or not.
Here are the commands you can try safely:mysql --version
mysqld --version
Another method is to use “dpkg” to list all the packages installed on the system, and specifically search for anything with “mysql” in the package name. For example:dpkg -l | grep mysql
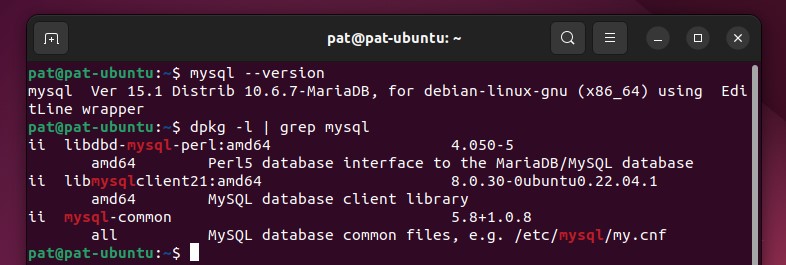
In this screenshot, you can see that the MySQL client is installed (it’s returning something with –version). The “dpkg -l” command is also telling me exactly which packages are installed (mysql-common, libmysqlclient and libdbd-mysql-perl).
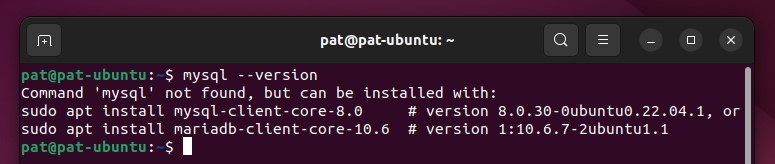
If MySQL is not installed, you’ll get an error “Command ‘mysql’ not found”, like on this example:
Download your exclusive free PDF containing the most useful Linux commands to elevate your skills!
Download now
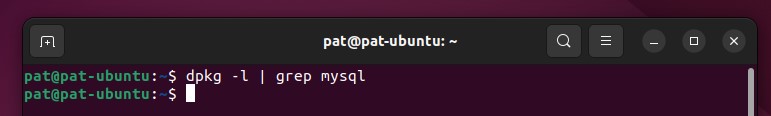
And the “dpkg” command will return nothing:
Using one of these commands should give you the answer you were looking for. Don’t forget that you may have the MySQL client installed, but not the server. That’s why there are two commands:mysql --version #client version
mysqld --version #server version (d=daemon)

If you’re new to the Linux command line, this article will give you the most important Linux commands to know, plus a free downloadable cheat sheet to keep handy.
How to know if MySQL is running?
The MySQL server is a service, which means it can be installed but not running. On Linux, you can use this command to check if it’s started:sudo service mysql status
Join Our Community!
Connect, learn, and grow with other Raspberry Pi enthusiasts. Support RaspberryTips and enjoy an ad-free reading experience. Get exclusive monthly video tutorials and many other benefits.
Learn moreOn my Ubuntu virtual machine, it looks like this:
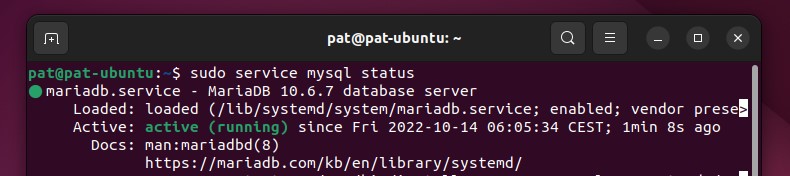
With colors, it’s pretty straightforward. I have a green mention “active (running)” on the third line, so my server is up and running. Most of the time, it will be “active” or “inactive”.
If MySQL is not running, you can start it with:sudo service mysql start
Then use the status command again to make sure it started correctly. If it doesn’t work, you may have an error in the status command output, or you can check the log files to find what’s going on.
How to check which MySQL version is running?
On Linux, the command “mysql –version” gives the version number of the MySQL client, while “mysqld –version” shows the version of the MySQL server (if installed).
While writing this article, I was using MariaDB 10.6.7, so I got something like this:
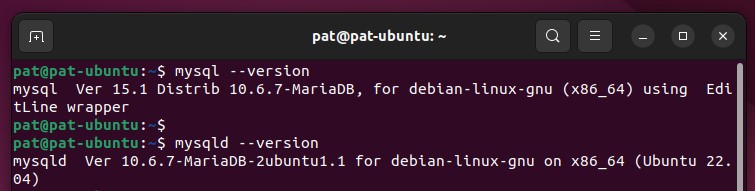
Even if MariaDB is now the most popular MySQL server package on Linux (and the default solution on most distributions I think), your server is not necessarily using it yet, so it will also answer this question.
Download your exclusive free PDF containing the most useful Linux commands to elevate your skills!
Download now
With these commands, I get the full description of the MySQL packages I’m using. In this case, I have MariaDB server and client installed, it’s version 10.6.7 in 64 bits, built for Ubuntu 22.04.
How to know which port MySQL is using?
By default, MySQL server is using port 3306. It can be changed in the configuration file, and a network scan or the “netstat” command can tell which port is currently used.
If you have access to the MySQL server, the easiest way is to use this query to get the information:sudo mysqlSHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'PORT';
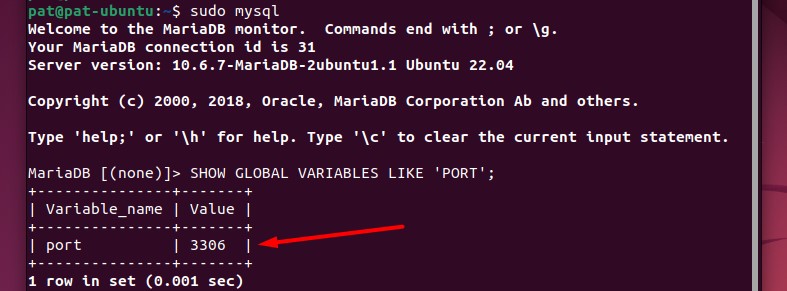
It will output a table with the port number.
But if you don’t know it, maybe you don’t have access to the MySQL server. In this case, the first thing you can try is to check the MySQL server configuration.
It’s located in /etc/mysql/my.cnf.
Display the MySQL configuration file with:cat /etc/mysql/my.cnf | grep port
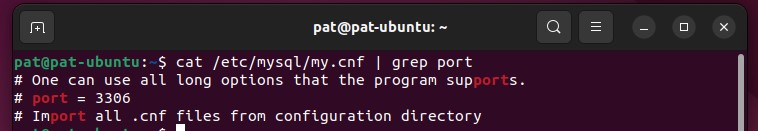
In this example, the port configuration line is still commented on, so it’s the default value (3306).
If there is no “#” at the beginning of the line, and another port is mentioned here, that’s the one you should try.
Another way is to use netstat, to see which services are running, and on which ports they are listening:sudo netstat -tlnp
Sudo is mandatory if you want to have the program name in the result, like this:
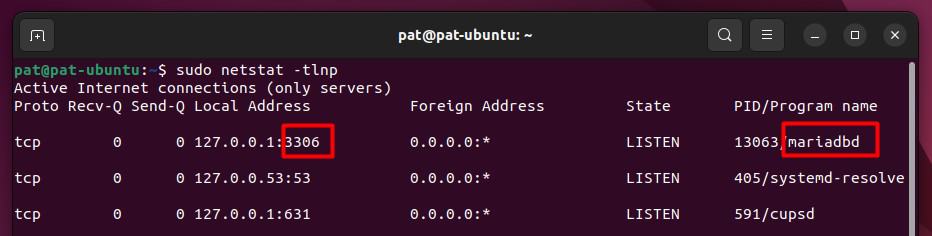
If your MySQL server is not using the default port, you need to specify it in the MySQL client command. Something like:sudo mysql --port=1234
Or:sudo mysql -P 1234
Where is MySQL located on Linux?
By default, MySQL data is stored under /var/lib/mysql on Linux, while the configuration files are under /etc/mysql.
Once again, you can use dpkg to list all the files associated with the MySQL server package:dpkg -L mariadb-server-10.6
This will give you something like:
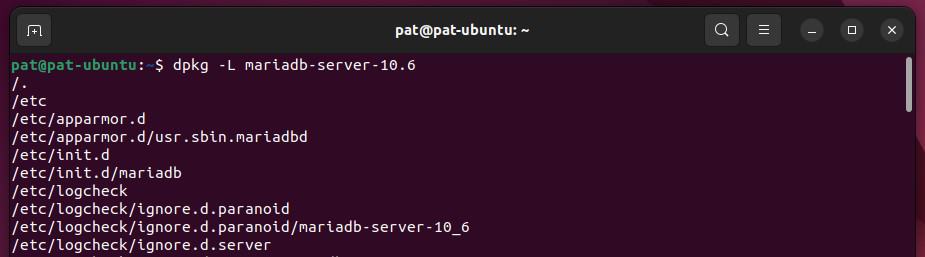
Where you can see exactly which files are being used by this package.
As a reminder, you can use:dpkg -l | grep mariadbTo know the exact package name (with the correct version).
Download your exclusive free PDF containing the most useful Linux commands to elevate your skills!
Download now
How to install MySQL?
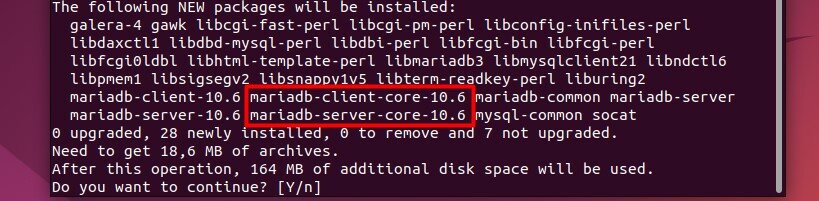
MySQL is available in the default repository on most distributions, but is most likely named “MariaDB”. It can be installed with “sudo apt install mariadb-server” for the server part, or “sudo apt install mariadb-client” for the client only.
The MySQL client will be installed automatically with the server, so you don’t need to specify both:
Once installed, the MySQL server needs to be initialized and configured. If you need a more step-by-step tutorial, you can read my dedicated article here: How to Install MariaDB? (MySQL Server).
I wrote it for Raspberry Pi, but it’s the same procedure on any Linux server.
And if your goal is to uninstall MySQL from your computer, you can click on the link to write my step-by-step procedure to do it safely.
Download your exclusive free PDF containing the most useful Linux commands to elevate your skills!
Download now
Want to chat with other Raspberry Pi enthusiasts? Join the community, share your current projects and ask for help directly in the forums.
Additional Resources
Overwhelmed with Linux commands?
My e-book, “Master Linux Commands”, is your essential guide to mastering the terminal. Get practical tips, real-world examples, and a bonus cheat sheet to keep by your side.
Grab your copy now.
VIP Community
If you just want to hang out with me and other Linux fans, you can also join the community. I share exclusive tutorials and behind-the-scenes content there. Premium members can also visit the website without ads.
More details here.
Need help building something with Python?
Python is a great language to get started with programming on any Linux computer.
Learn the essentials, step-by-step, without losing time understanding useless concepts.
Get the e-book now.