How to Install VMWare ESXi on a Raspberry Pi? (Step by step)
VMWare ESXi is a virtualization system, allowing us to run several virtual machines on the same host. VMWare recently released an ARM version, so that we can install it on Raspberry Pi.
But … how to say … we have already seen easier systems to install 🙂
The official installation guide is almost 20 pages long, but I will summarize it here for you.
VMWare ESXi Arm Edition is available on the VMWare Flings website.
Before the installation, there are a few settings to change in the Raspberry Pi BIOS.
After that, the system can be installed on a USB key and will run from there.
In this short introduction, it may seem easy, but I can guarantee it’s probably the most complicated system I’ve ever installed on my Raspberry Pi.
So stay tuned, as I’ll explain everything step-by-step, so that you can do it by your side anyway.
Before installing VMWare ESXi
Before going to the installation part, let me introduce a bit what we will do and what you need to know and do in this tutorial.
What is VMWare ESXi?

VMWare ESXi is a well-known software for virtualization purposes in many companies (an alternative to Microsoft Hyper-V, also very popular).
For example, I’m using it at work, to run several Linux systems, and host different services on each one.
This avoids having a physical server for each system, and also allows advanced features like clustering, high availability and full backups.
That’s it for the general idea, my goal here is now to go too far in the VMWare ESXi introduction.
If it’s the first time you hear about it, it’s probably a good idea to look for more details before going further here.
But whatever your current level, I’ll show you how to install it on your Raspberry Pi.
So, VMWare has now an ARM version of the ESXi system.
It’s available under the Flings brand for the moment (like a lab if you want, not a complete support in the main product), and it works well on Raspberry Pi (at least on a Pi 4 with 4GB RAM or more).
As a side note, you can also install Proxmox on Raspberry Pi. I tried it too, it’s not there yet, but it’s almost ready.
Raspberry Pi installation overview
As I told you, the installation procedure is not the easiest one for a system install.
There are several steps we need to see:
- Prerequisites: you’ll need an SD card as usual, but also at least two USB drives to install VMWare ESXi on your Raspberry Pi. I’ll explain why later.
- Step 1 – UEFI Bios: We’ll need to boot the UEFI firmware to use VMWare ESXi. This is the main goal of the SD card in this installation. We’ll access the Raspberry Pi BIOS, change a few things and then boot on a USB drive.
- Step 2 – Installation: The installation wizard for VMWare ESXi will be on a USB key, we’ll boot on it to install the system somewhere (can be the same USB key or another one).
- Step 3 – Storage: Once on the ESXi system, you’ll need another USB storage to run the virtual machines on it. On a standard server it’s the same thing, the system and the virtual machines datastore are not on the same disk(s). So, step 3 will be to configure this storage space.
- Step 4 – Create a virtual machine: Finally, I’ll show you how to create your first virtual machine. Once everything else is done, it’s the same process as on any server.
Now that you understand the big picture, let’s see the details 🙂
It's a free PDF guide containing every Raspberry Pi Linux command you should know!
Download now
Prerequisites
To sum up, here is what you need to get started:
- A Raspberry Pi: I would recommend a Raspberry Pi 4 with 8GB RAM if you really want to use this system on the long term. If it’s just to test it, a Raspberry Pi 4 is still required, but 4GB is ok.
- An SD card: Any model will be ok, it’s only to start the UEFI boot, so we’ll not really use it once VMWare started.
- A first USB drive: This one will store the ESXi installation image, but it can also run the system after that. So depending on your goals, it can be a basic USB key or an SSD USB drive for better performances. You don’t need so much space, 16GB is enough.
- Another USB drive: The previous one will be for the system installation, this one is to host the virtual machines. For this one, a SSD USB disk seems really useful as it will directly impact the performances of your virtual machines.
- (Optional) a third USB drive: I find a bit weird to overwrite the installation USB key with the system. So another option is to have a third USB drive for the final installation of VMware ESXi. It’s useful to keep the installation key intact, in case you need to reinstall it later for example.
If you are using USB drive(s) instead of USB keys, make sure they are self-powered, or use a powered USB hub.
The Raspberry Pi will probably not have enough to power two or three USB drives simultaneously.
Once you have everything ready, you can move to the installation part.
Install VMWare ESXi ARM Edition
Update the Raspberry Pi Firmware
The first thing to do is to update the Raspberry Pi firmware to enable the USB boot feature.
If you already used this feature in the past, you can skip this step, you only need to do this once for each Raspberry Pi.
If not, here is the procedure:
Join Our Community!
Connect, learn, and grow with other Raspberry Pi enthusiasts. Support RaspberryTips and enjoy an ad-free reading experience. Get exclusive monthly video tutorials and many other benefits.
Learn more- Start on a Raspberry Pi OS system if you have one, or flash a new SD card with Raspberry Pi OS on it (the Lite version is enough).
Check this tutorial if you need further assistance about this. - Update the system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt full-upgrade - Update the firmware:
sudo rpi-update
sudo rpi-eeprom-update -d -a
After a reboot, your Raspberry Pi can now boot on USB.
Note: another way to do this is to use the EEPROM boot recovery image in the Raspberry Pi Imager.
Prepare the SD card
Then, we can create the SD card.
As I explained previously, the only thing we need on this SD card is the Raspberry Pi UEFI firmware, to access the BIOS and boot VMware from there.
- Format the SD card in FAT32.
If you just used the SD card to update the firmware, you just need to erase everything on it (or format the partition).
If it’s a brand new SD card, you’ll need to use the tool from your operating system to create a new partition.- On Windows, you’ll probably get a prompt asking you to format it once plugged. Or you can go to the disk management tool and create the partition in it.
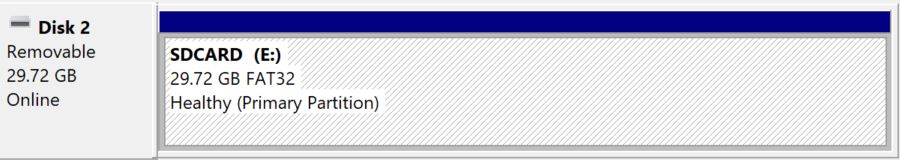
- On Linux, you can use the command line (tutorial here) or use a tool like Gparted to do this from the GUI.
- On Windows, you’ll probably get a prompt asking you to format it once plugged. Or you can go to the disk management tool and create the partition in it.
- Download these two files:
- Extract them, each one in a separate folder
- Go into the first folder (firmware-master).
Copy all the files from the boot subfolder to your SD card, except the ones starting with “kernel” - Then go into the second folder (RPI4_UEFI_Firmware_vX.X)
Copy all the files to the SD card.
Confirm overwrite when asked.
The SD card is ready to use, you can insert it in your Raspberry Pi, but don’t start it for the moment.
USB key preparation
The second step is to create the USB key with the VMWare installation image.
Here is how to do this:
- Go to the VMWare Flings website and download the ARM ISO file.
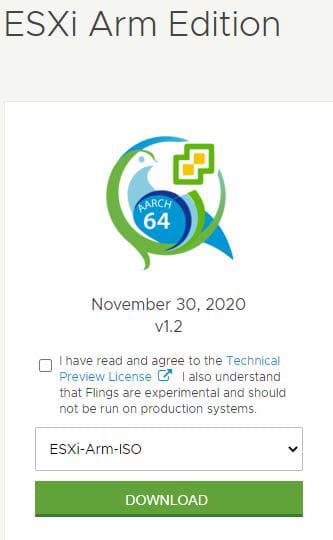
- A VMWare account is required to access the file download.
You’ll get an evaluation license for 180 days, but can still use it for free after that (with fewer features, but the most important ones stay enabled). - Once the file downloaded, you can use a tool like Balena Etcher to flash it on your USB key:
- Download and install Etcher if needed
- Start the application, a window like this shows up:
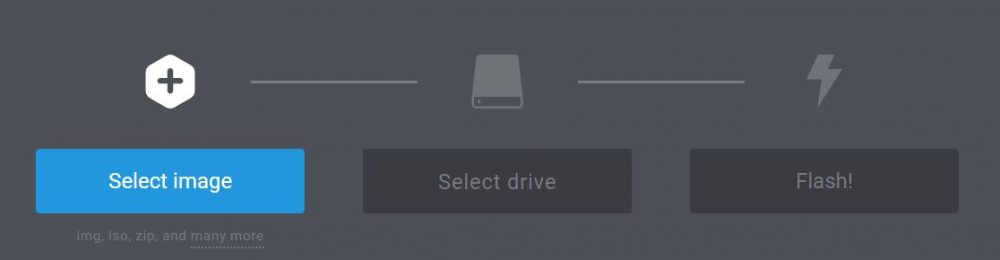
- Select the VMWare ISO file on the left, then your USB key and click on “Flash!” to start the process.
- You’ll get a warning because it’s not a bootable image, confirm to continue.
After a few seconds, the USB key is ready, you can plug it on your Raspberry Pi, and the next step is to access the BIOS menu to start the installation wizard.
BIOS Settings
Start the Raspberry Pi with the SD card and the USB key plugged.
Then follow these steps:
- Just after the rainbow screen, you’ll see a screen you have probably never seen before:

- Press “ESC” to access the BIOS menu
- Then go to Device Manager > Raspberry Pi Configuration > Advanced Configuration
You can use the arrows and “Enter” keys to move in this menu. - Disable the 3GB RAM limit:
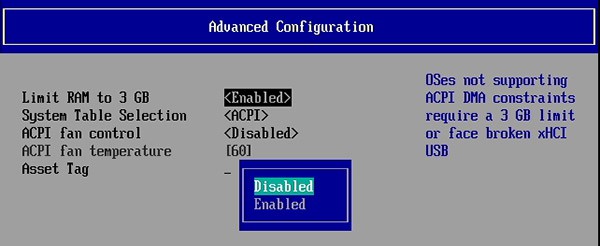
- Press “ESC” a few times to get back to the main menu, and confirm with “Y” to save the change.
- Then go to “Boot Maintenance Manager” > “Boot Options” > “Change Boot Order”
- Here you can set the USB key as the first boot device
(Press “+” to move it to the top).
Choose “Commit changes and exit”. - Then, on the main menu, click on “Continue” to exit the BIOS and start the VMWare installation.
If you get something like that, you are good:
Wait a few minutes for the system to start (it’s time for coffee break at this point!), and move to the next step.
It's a free PDF guide containing every Raspberry Pi Linux command you should know!
Download now
VMWare Installation
If you chose the installation with a third USB drive, you need to plug one now.
Once the yellow screens disappears, you’ll get a setup menu to install the system.
This is straightforward, here are the steps:
- On the first message, press “Enter” to continue
- Accept the License agreement with “F11”
If you are using the same keyboard as me, it’s probably something like “Fn+F9” to do “F11” - The wizard will scan your locale devices, and display the available USB drives to install the system.
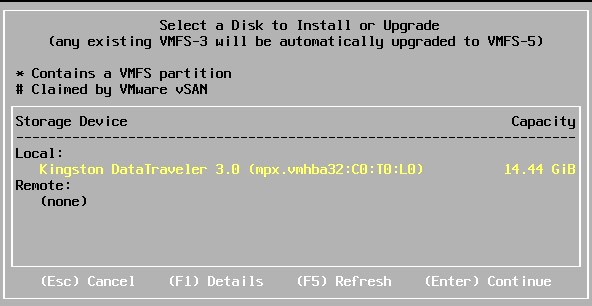
If you have only one, it’s easy, press enter to continue.
If you have two or more, select the one where you want to install the system (you’ll need to keep it plugged all the time after that). - Then select the keyboard layout and press “Enter” to continue.
- Finally, enter the root password.
You need something with several character types, I don’t know exactly the rules, but try something like letters, numbers and special characters. - Now, you just need to start the installation by pressing “F11”
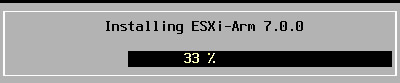
The installation will take more or less time depending on the devices you are using, but basically, it’s something like 10 minutes on a basic USB key.
The wizard ask you to remove the installation media, obviously do this only if you have two USB keys at least. With one only, the system is now on the USB drive so you need to keep it plugged.
The SD card is also required for the system to start automatically.
First boot on ESXI
Press “Enter” at the end of the installation to reboot the Raspberry Pi.
The Raspberry Pi should start automatically with the SD card, that will boot the USB key first.
If it’s not the case, get back into the BIOS menu, you probably need to fix the boot order (especially if you are using a different USB key).
After that, you’ll get the yellow screen again, and the VMWare ESXi system will start.
There is nothing to do at this step.

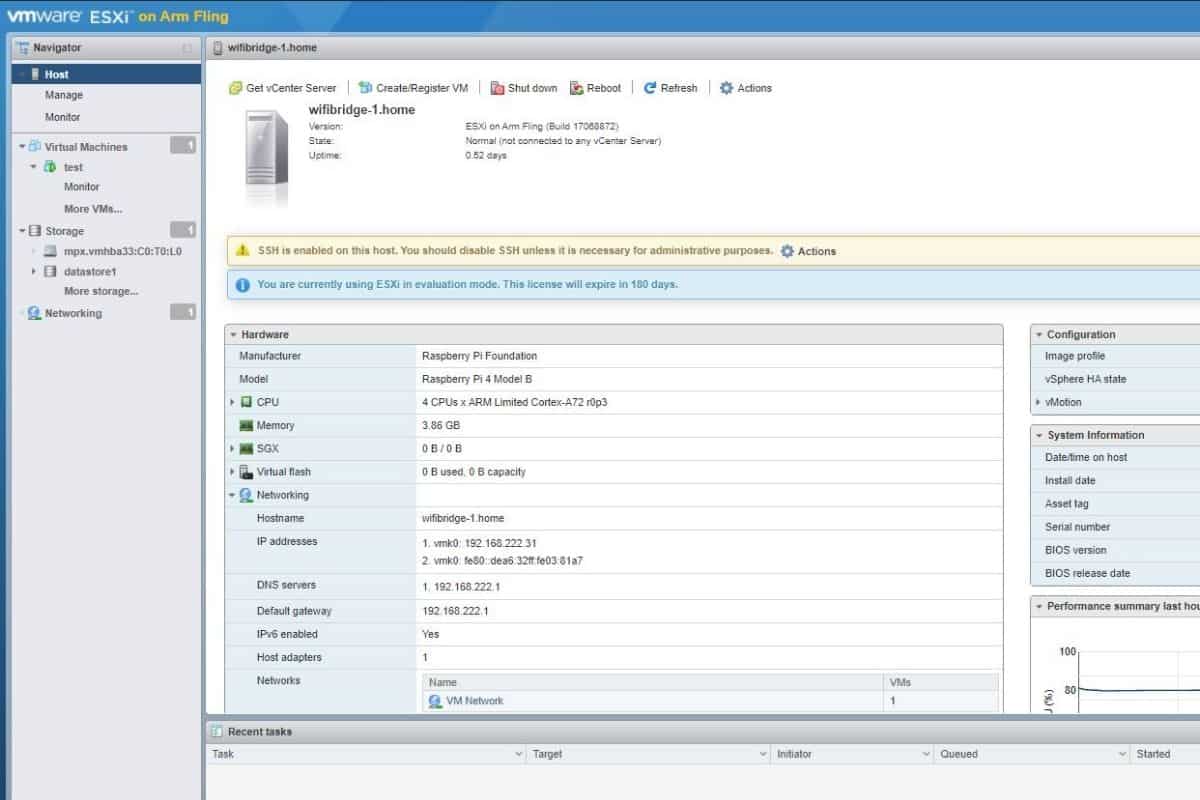
Once the system is completely started, you can access the web client at: http://<IP>.
The IP address is visible on your screen.
Going further with VMWare ESXI
Ok, all of this is good, VMWare ESXi is now installed on your Raspberry Pi.
But now you’ll probably need a bit more help to use it and create your first virtual machine on it.
If you are used to ESXi, it’s almost the same as usual, there is just a tip I will give you to create the datastore because I had trouble finding the solution.
Create a datastore
Creating a datastore is not possible by default on ESXi.
When you plug a USB drive, it will be mounted automatically, so that you can use it in a virtual machine easily.
But to create a storage partition on it, you need to follow these steps:
- Log in into the web client.
The username is “root” and the password you chose during the installation.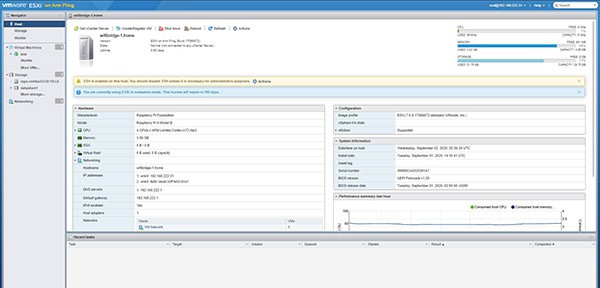
- Enable SSH
Do a right click on “Host” in the left menu
Go to “Services” and click on “Enable secure shell (SSH)” - Use Putty or any other SSH client to access the Raspberry Pi prompt.
- Log in with the same username and password
- Enter the two commands:
/etc/init.d/usbarbitrator stop
chkconfig usbarbitrator off
This will stop the USB service that auto-mount USB drives, and disable it on boot. - Plug your USB drive.
Try to use the USB 3.0 ports (blue), that are faster, for this datastore at least (ideally, both drives should be on them, but it’s not always possible). - Just to be sure, convert the USB key to msdos instead of gpt
Maybe it’s not required on your system or with your drive, but as I’m on Windows, all my USB keys are using the GPT format.- Get the device ID in the web client
Go to Storage > Devices.
Click on the USB drive you want to use (you may need to unplug/plug it to refresh the view, now that the USB arbitrator service is off).
Note the “Path” field. - Switch to msdos with the following command:
partedUtil mklabel /dev/disks/mpx.vmhba32:C0:T0:L0 msdos
The device path might be different on your system.
I didn’t manage to create the datastore before doing this.
- Get the device ID in the web client
- You can now create the datastore from the web client (the storage disk for your virtual machines):
- Go to Storage > Datastores
- New datastore
- Choose a name for this datastore (datastore1 for example).
- Select the USB device you want to use
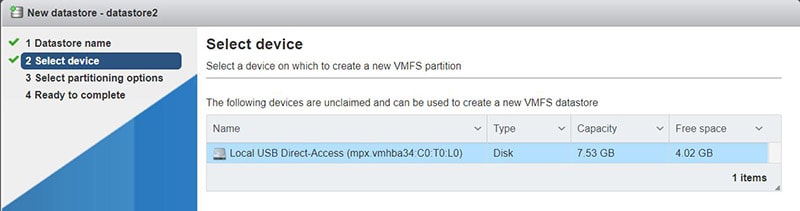
By the way, this is a random USB key just for the screenshots, I’m not using this one 🙂 - Then select the partitioning options.
“Use full disk” would be my recommendation as you’ll keep it plugged all the time. - And click on Finish to format the drive and create the new datastore.
Wow, that’s it, you datastore is ready to use.
That’s all for the special tricks you need to know about installing ESXi on Raspberry Pi, but if you are new on this system, I’ll also guide you to create the first virtual machine.
Create a virtual machine
We have the system installed, a datastore ready to store virtual machines, we just need to create them now 🙂
Here is the procedure to create a new virtual machine:
- Click on “Virtual Machines” in the left menu
- Click on “Create / Register VM”
- A wizard shows up, asking you if you want to create a new one, deploy a pre-built machine or register an existing one.
I’ll show you the first case, and you can find help easily on the web for the two other ones. - Then, enter the name of the virtual machine and the operating system you will install on it:
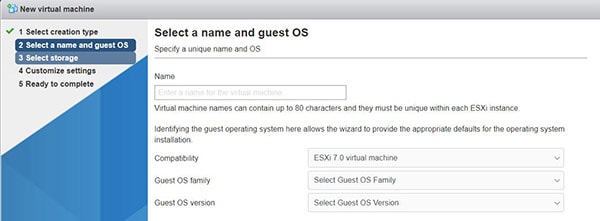
- Select the storage you want to use.
It’s probably the “datastore1” we just created. - Then you can customize the virtual machine configuration:
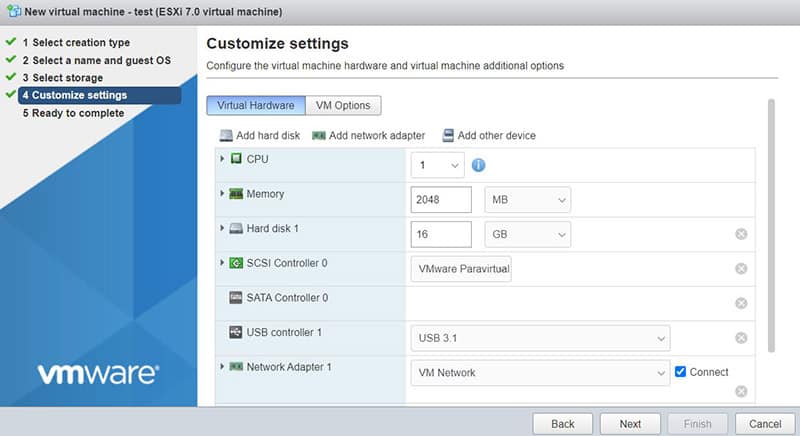
Don’t forget that you are on a Raspberry Pi, so the resources are not unlimited. - For the CD/DVD drive line, choose “Use datastore iso file” and upload an image with the system you want to use
The easiest one for a first try is to use the Debian ARM64 net installer image (available here).
For other distributions, look at what you can find, or follow the tutorials on the website I link below (you will probably need to use qemu to convert the image file into a VMWare disk file). - Click “Next” and “Finish” to complete the virtual machine creation.
The virtual machine is now available, you just need to start it to install the system on it.
To interact with the virtual machine, you can use the HTML viewer, or install the remote console for more features and better keyboard support (especially if like me, you are not using a US keyboard).
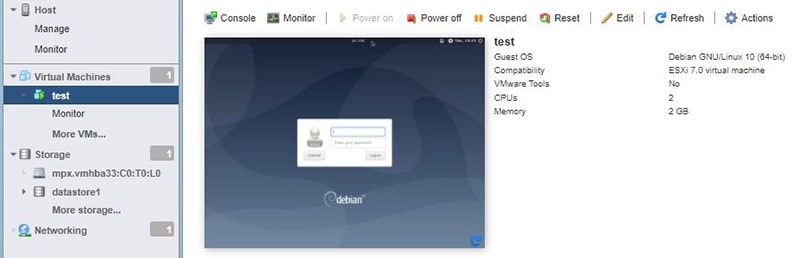
The installation of Debian took a very long time for me (a few hours), but I’m not on an optimized setup at all, so it’s probably better with a decent drive (hopefully).
If you want to install VMware Tools on your new virtual machine, click the link to read my tutorial on how to do so.
If you want to go further with ESXi-ARM, I really recommend this website, that includes many tutorials to install specific systems on it or advanced configuration tips.
It's a free PDF guide containing every Raspberry Pi Linux command you should know!
Download now
Video
You can check this video from my YouTube channel, to watch me installing VMware ESXi on my Raspberry Pi:
It's a free PDF guide containing every Raspberry Pi Linux command you should know!
Download now
Reminder: Remember that all the members of my community get access to this website without ads, exclusive courses and much more. You can become part of this community for as little as $5 per month & get all the benefits immediately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this VMWare ESXi version for the ARM architecture works pretty well. The installation is a bit complicated the first time, as you need to understand the different steps, but hopefully, my guide here is easier than the official one 🙂
In real life, I’m not sure if I will use this system as I don’t really see a case where it can be useful for me. But if you are hosting different services, want to test x64 systems or anything else, you can now do this on Raspberry Pi directly.
The alternative being to use VMWare Workstation on your PC, and run Raspberry Pi OS in it.
Whenever you’re ready, here are other ways I can help you:
The RaspberryTips Community: If you want to hang out with me and other Raspberry Pi fans, you can join the community. I share exclusive tutorials and behind-the-scenes content there. Premium members can also visit the website without ads.
Master your Raspberry Pi in 30 days: If you are looking for the best tips to become an expert on Raspberry Pi, this book is for you. Learn useful Linux skills and practice multiple projects with step-by-step guides.
The Raspberry Pi Bootcamp: Understand everything about the Raspberry Pi, stop searching for help all the time, and finally enjoy completing your projects.
Master Python on Raspberry Pi: Create, understand, and improve any Python script for your Raspberry Pi. Learn the essentials step-by-step without losing time understanding useless concepts.
You can also find all my recommendations for tools and hardware on this page.